V1 - Command - where
The where command has similar syntax with search, and all the query functions above associated with search can be used after where.
The difference between where and search is that where is used after the variables extracted from database. If the query of where returns false, the corresponding columns are discarded. An example of combining two commands is given:
search {from="-7d@d", to="@d"} sContent("@eventType","nxlogAD")
let {sourceIPAddress,eventSource,eventName} =f("@cloudtrail")
where eventSource=="iam.amazonaws.com" and sContains(eventName,"Describe")==false
The 'where' command
The where command uses the following syntax:
where query
The "query" parameter consists of expressions and boolean operators and, or and not:
expression1 and expression2 ... expressionN
Example:
search {time} expression1 and expression2 not expression3 ... expressionN
Usage examples
Example:
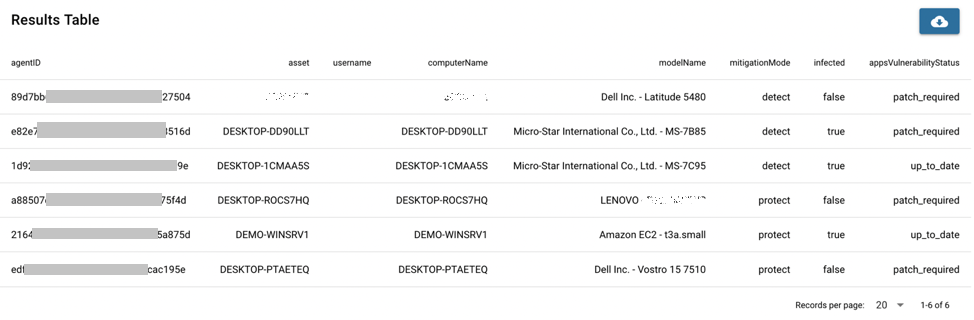
load resource sentinelOneAgent
let {agentID, asset, username} = f("@sentinelOneAgent.translation")
let {computerName, modelName, mitigationMode, infected, appsVulnerabilityStatus} = f("@sentinelOneAgent")
where infected==true or appsVulnerabilityStatus=="patch_required"
With the command where, only the events which are marked as true of "infected" or "patch_required" of "appsVulnerabilityStatus" are kept in the results.